Are you at the start of your SEO journey? Maybe you’ve heard that SEO can help drive traffic to your website and get you higher rankings, but you aren’t really sure how it works or what areas to focus on? Well, you’ve come to the right place. Read on to find out what every digital marketer should know about SEO.
Defining Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Let’s start by asking an obvious question: what exactly is SEO? Well, SEO stands for ‘Search Engine Optimization’, which is the process of getting traffic from free, organic, editorial, or natural search results in search engines. It aims to improve your website’s position in search results pages. Remember, the higher the website is listed, the more people will see it.
- Good SEO involves many different activities, such as:
- Identifying relevant keywords with good search traffic potential
- Creating high-quality, useful content and optimizing it for search engines and for users
- Including relevant links from high-quality sites
- Measuring the results
These days, SEO is considered an essential marketing activity.
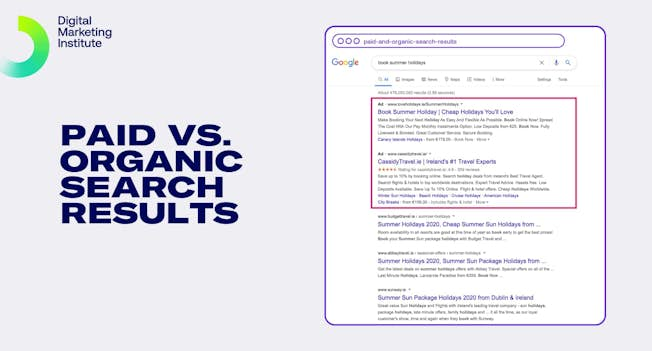
Differences between paid and organic search
From the outset, it’s important that you understand the differences between the organic, natural search synonymous with SEO and paid search. There are five key differences:
Position
The first difference is that paid search results appear at the top of search engine results pages, and organic results appear beneath them.
Time
Another key difference between paid and organic search is time. With paid search, you get near instant results, sometimes in minutes; whereas, with organic search, results take more time - often weeks, months, and even years. So you have to play the medium to long-term game with organic search.
Payment
When it comes to paying, well, as the name suggests, with paid search traffic is paid. You pay-per-click (PPC) on a cost-per-click (CPC) basis. What that means is, you pay a fee every time a user clicks on your ad. So instead of relying on organic traffic to your website, you buy traffic for your page by paying Google to show your ad when your visitor does a search for your keyword. For organic search, traffic is free, although it does require an investment of both resources and time.
ROI
In terms of the return on investment or ROI, it's actually much easier to measure with paid search. That's partly because Google provides more keyword data that you can capture in Google Analytics. However, with paid search, ROI can stagnate or decline over time. With organic search, ROI is a little bit harder to measure, but it often improves over time. Over the long term, organic search can offer a very good return on investment.
Share of traffic
When it comes to the share of traffic, roughly 20% to 30% of searchers click on paid results, and 70% to 80% of searchers click on SEO results. So the lion’s share of clicks are actually on the organic results.
Similarities between paid and organic search
It’s not all about differences – there are also similarities between paid and organic search:
- Keyword research: You use a search engine for both paid and organic search, and both require a user to enter a keyword. So you need to do keyword research for organic search and paid search.
- Landing pages: Both types of search require you to create landing pages. For SEO, the landing page needs to be connected to your website. For paid search, it can be the exact same landing page you use for organic, or it can be a completely separate stand-alone page that sits off your website.
- Traffic: Generating traffic is a major goal of both paid and organic search. Most importantly, both paid and organic search traffic includes user intent. That is, someone is asking Google a question or searching for information – they are in an active mindset and as a result they are more likely to take action once they find this information.
The three pillars of SEO
As a digital marketer, knowing how to get your brand, website, or company found by searchers is a core skill, and understanding how SEO is evolving will keep you at the top of your game. While SEO changes frequently in small ways, its key principles do not. We can break SEO into three core components or pillars that you need to be familiar with – and action regularly:
- Technical Optimization: Technical Optimization is the process of completing activities on your site that are designed to improve SEO but are not related to content. It often happens behind the scenes.
- On-Page Optimization: On-Page Optimization is the process of ensuring the content on your site is relevant and provides a great user experience. It includes targeting the right keywords within your content and can be done through a content management system. Common examples of content management systems include WordPress, Wix, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, Shopify, and Expression Engine.
- Off-Page Optimization: Off-Page Optimization is the process of enhancing your site’s search engine rankings through activities outside of the site. This is largely driven by backlinks, which help to build the site’s reputation.

How do search engines actually work?
Search engines are used by people when they have a query and are searching on the internet for the answer. Search engine algorithms are computer programmes that look for clues to give searchers the exact results they are looking for. Search engines rely on algorithms to find web pages and decide which ones to rank for any given keyword. There are three steps to how search engines work: crawling, which is the discovery stage; indexing, which is the filing stage; and ranking, which is the retrieval stage.
Step 1: Crawling
The first step is crawling. Search engines send out web crawlers to find new pages and record information about them. We sometimes call these web crawlers ‘spiders’ or ‘robots’. Their purpose is to discover new web pages that exist, and also to periodically check the content on pages they’ve previously visited to see whether they've changed or been updated.
Search engines crawl web pages by following links they’ve already discovered. So if you have a blog post and it's linked from your homepage, when a search engine crawls your homepage, it will then look for another link to follow and may follow the link to your new blog post.
Step 2: Indexing
The second step is indexing. Indexing is when a search engine decides whether or not it is going to use the content that it has crawled. If a crawled web page is deemed worthy by a search engine, it will be added to its index. This index is used at the final ranking stage. When a web page or piece of content is indexed, it is filed and stored in a database where it can later be retrieved. Most web pages that offer unique and valuable content are placed into the index. A web page might not be placed in the index if:
- Its content is considered duplicate
- Its content is considered low value or spammy
- It couldn’t be crawled
- The page or domain lacked inbound links
Step 3: Ranking
The third step is really the most important step, and that is ranking. Ranking can only happen after the crawling and indexing steps are complete. So once a search engine has crawled and indexed your site, your site can be ranked.
There are more than 200 ranking signals that search engines use to sort and rank content, and they all fit under the three pillars of SEO: technical optimization, on-page optimization, and off-page optimization. Some examples of signals that search engines use to rank web pages are:
- Keyword presence in title tag – Whether the keyword or a synonym was mentioned on the page and within the title tag
- Loading speed of web page – Whether the web page loads quickly and is mobile-friendly
- Website reputation – Whether the web page and website is considered reputable for the topic being searched for

Ordering and ranking results
Google’s main search algorithm is called Google Hummingbird, and it is responsible for deciding how to order and rank search engine results.
Google also has a machine-learning search engine sub-algorithm called RankBrain:
- If RankBrain sees a word or phrase it isn’t familiar with, it uses artificial intelligence to understand it better by connecting it to similar search queries.
- It allows Google to understand these queries by converting keywords into known topics and concepts, meaning it can provide better search engine results – even when queries are unusual.
- Rather than attempting to be the best keyword optimized result, RankBrain rewards websites that provide user satisfaction and return the result that the user expects.
Getting the most out of RankBrain
A good SEO strategy is to optimize your website to improve user experience and satisfaction, and try to get the most out of the RankBrain ranking factor.
The three most effective ways to do this are:
- Optimize for medium-tail keywords (key terms consisting of two to three words).
- Optimize page titles and descriptions for clicks so that when someone searches, your listing is more likely to be clicked. The click-through rate is the percentage of people who see you on Google and then go ahead and click through to your website.
- Optimize content to increase dwell time (the length of time people stay on the page) and reduce bounce rate (the percentage of visitors who leave after only viewing one page).
Remember, Google’s top three ranking factors are:
- Links
- Content
- RankBrain
Setting SEO objectives
Setting SEO objectives is a vital part of any SEO strategy. It is important to set SEO objectives – and to align them with your overall business objectives – because:
- They encourage buy-in from key stakeholders.
- They help you to formulate your SEO strategy.
- They ensure goals are met.
What should you measure?
While it can feel like a laborious task to set objectives, measuring them can really help you make progress with your SEO in the long term. So what types of things should you measure?
Consider measuring:
- Keywords
- Traffic
- Market share
- Brand awareness
- Lead generation
- Reputation
- E-commerce
Examples of SEO objectives
Here are three examples of SEO objectives that can be used as a guide to setting relevant objectives for your own business or website:
"Move 50% of our top 20 keywords onto the first page of Google within nine months." This objective focuses on keyword ranking.
"Improve our year-on-year organic traffic by 20% in quarter three and 25% in quarter four." This objective focuses on increasing organic website traffic.
"Grow our SEO market share from 3% to 5% in the next financial year." This objective focuses on growing market share.
Setting objectives for different types of businesses
The focus of your objectives will vary depending on whether your business is transactional or informational.
If your business is transactional and you have an e-commerce element, you’ll want to set your objectives around tracking sales and lead conversions. However, if you're a non-ecommerce commercial site, you’ll want to focus on lead generations.
If your business is informational, you are more likely to set objectives focusing on brand awareness or website traffic.
Finally, remember, even when you have fully implemented your SEO strategy, SEO is never finished. With SEO, you may need to change tactics midway through, play a long game, and wait to see the end results. But with a solid SEO foundation in place – and a little patience – the benefits of your SEO strategy should become apparent, leading to a better user experience for customers and more conversions for your business.
- Categories:
- Articles
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
Upgrade to Power Membership to continue
your access to thousands of articles, toolkits, podcasts, lessons and much much more.
Become a Power Member- Login
- View Courses
- - - -
- Courses
- Resources
- - - -
- My Account
- Change Password
- Logout